Brief infomation about farm ponds
Irrigation would be the logical solution but water scarcity, depleted ground water, and the high costs of irrigation infrastructure are major handicaps. Alternative solutions are needed to increase the quantity of water for farmers’ fields – solutions that are affordable, effective, eco-friendly and beneficial for the poor. Water harvesting, the capture and storage of rainwater for use during dry periods, is a technology proven to increase food security in drought prone areas. Erosion control and groundwater recharge are additional advantages of water harvesting techniques, which contribute to agricultural development and resource conservation. There are many types of water harvesting structures. At the household level, one of the most effective systems is the farm pond. A farm pond is a dug out pond constructed in or near the farm. Rainwater is collected in the pond and stored for future uses such as irrigating crops, recharging groundwater, and providing drinking water for farm animals.:
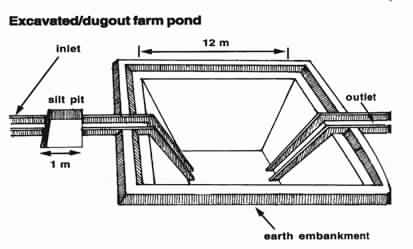 A test pit is dug out before finalizing the location and depth of excavation. The excavation and transportation of earth can be accomplished with a combination of manual labour or with machines like excavators and tractors. Soil conditions must be carefully considered. Excavation in areas with hard clay soil, such as Ramnad district, is very difficult and expensive using manual labour.
A test pit is dug out before finalizing the location and depth of excavation. The excavation and transportation of earth can be accomplished with a combination of manual labour or with machines like excavators and tractors. Soil conditions must be carefully considered. Excavation in areas with hard clay soil, such as Ramnad district, is very difficult and expensive using manual labour.- Use of machines for excavation and transportation is the best method in this context, with human labour used for levelling, bund formation, and construction.
- They provide water to start growing crops, without waiting for rain to fall.
- They provide irrigation water during dry spells between rainfalls. This increases the yield, the number of crops in one year, and the diversity of crops that can be grown.
- Bunds can be used to raise vegetables and fruit trees,thus supplying the farm household with an additional source of income and of nutritious food.
- Farmers are able to apply adequate farm inputs and perform farming operations at the appropriate time, thus increasing their productivity and their confidence in farming.
- They check soil erosion and minimizes siltation of waterways and reservoirs.
- They supplies water for domestic purposes and livestock
- They promote fish rearing.
- They recharge the ground water.
- They improve drainage.
- The excavated earth has a very high value and can be used to enrich soil in the fields, leveling land, and constructing farm roads.








